close
L
O
A
D
I
N
G
- Open Hours: Mon-Fri 8:00 am-6:00 pm
- Email: ewastestar@gmail.com
- Address: 6A Anvil Way, Welshpool WA 6109, Australia
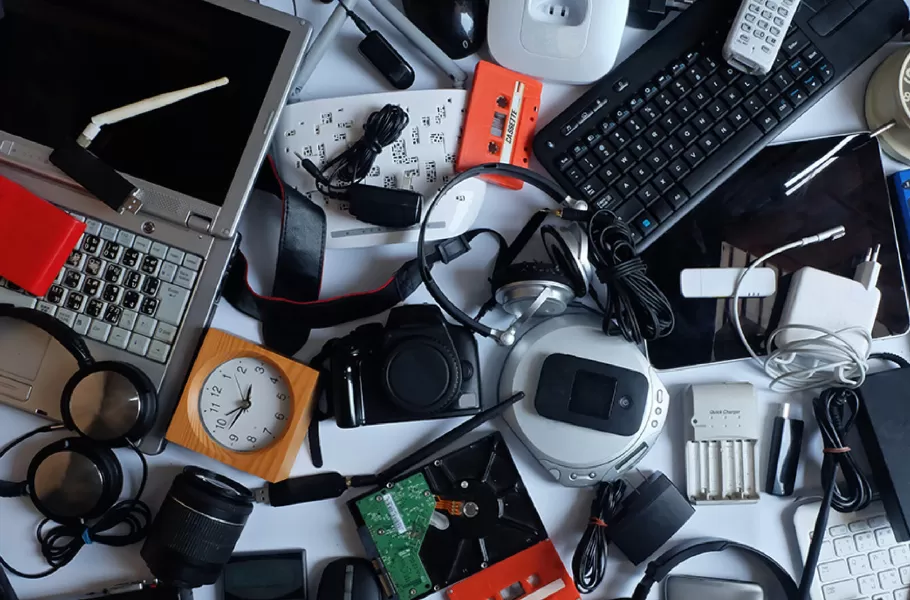
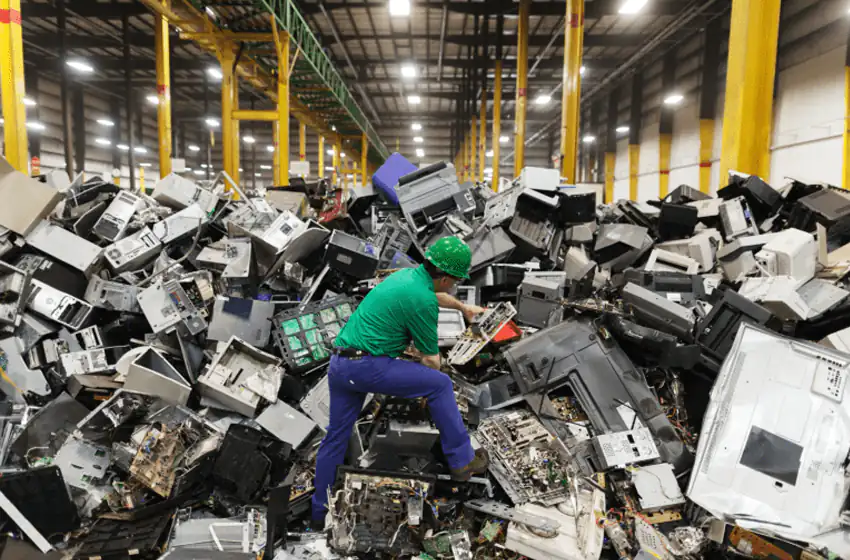
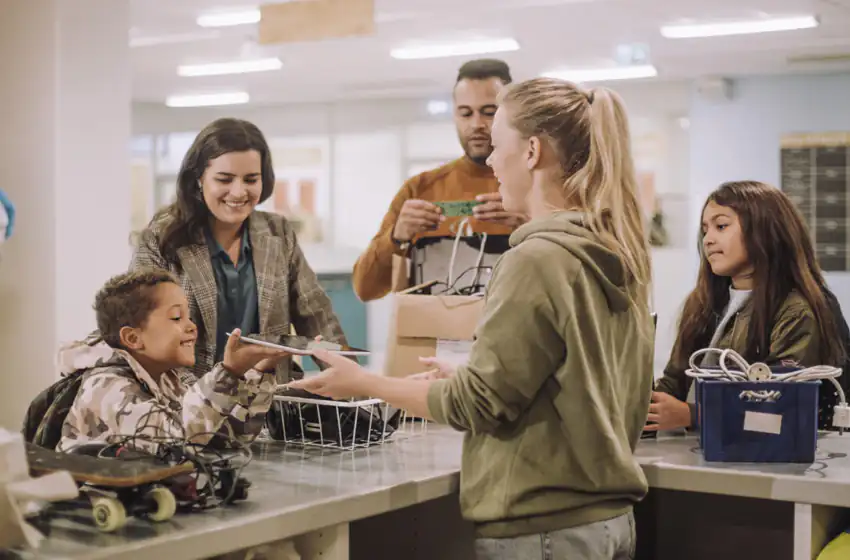
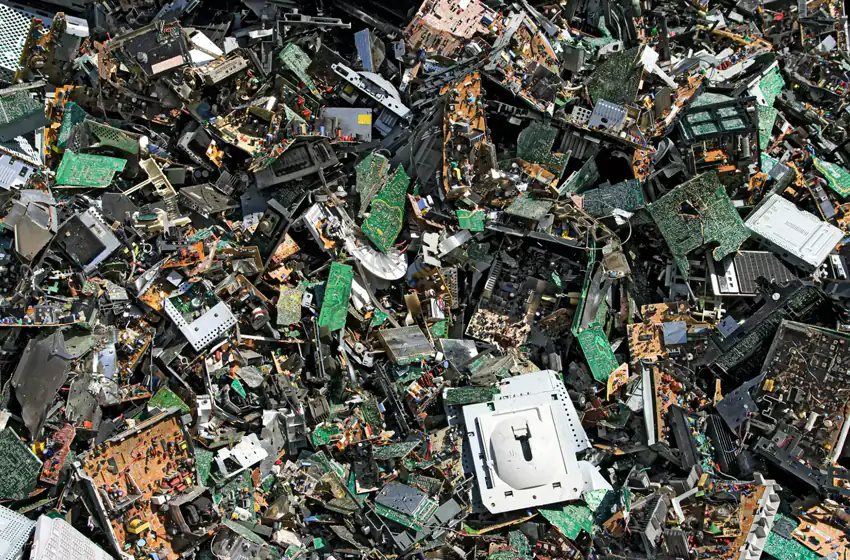
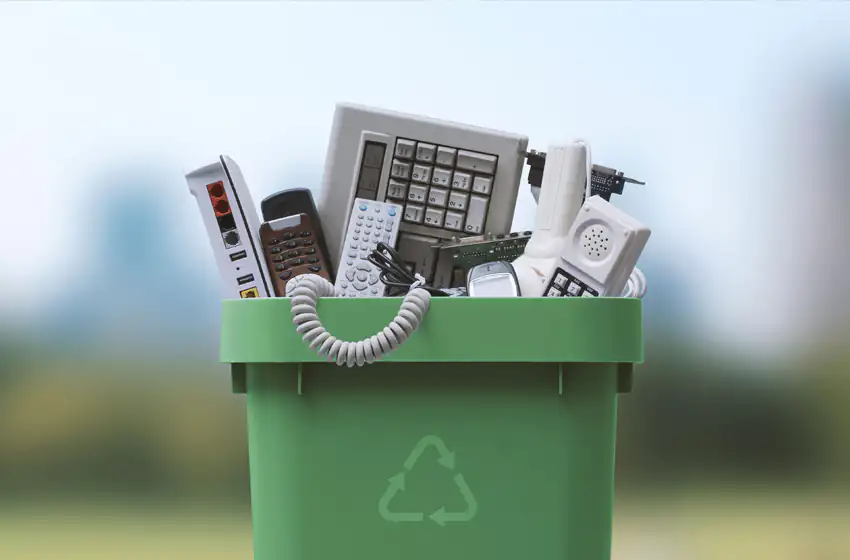
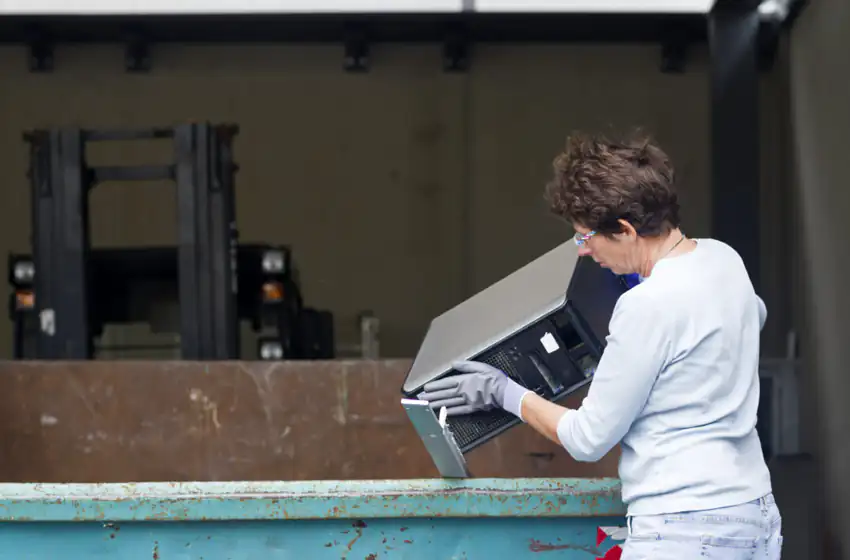
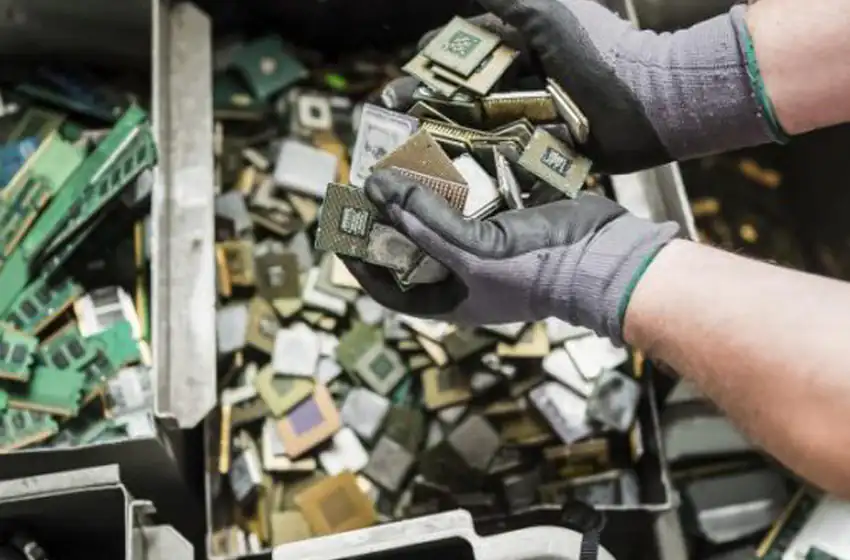
The Complete Guide to Electronics Recycling: A Step-by-Step Process Explained